At Novo Nordisk, we are acting on our purpose to defeat diabetes and other serious chronic diseases by expanding our commitment in areas of high unmet need, including cardiovascular disease (CVD). This is a disease that impacts millions of people worldwide,1 and we welcome you to learn more about its causes, symptoms, and how you can look after your heart health, as well as discover our research and development efforts within this disease area.
Cardiovascular disease is an umbrella term for conditions that affect the heart or blood vessels.1,2 There are many different types of cardiovascular disease, with some of the most common being coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, heart failure and peripheral artery disease.
The most common cause of coronary heart disease is atherosclerosis,3 an inflammatory condition in which arteries become narrowed (stenosis) due to the accumulation of fatty substances called plaques.4
Some of the most important factors that can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease are smoking, obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol levels, and high blood pressure.5,6
As these conditions become more prevalent around the world, cardiovascular disease poses a significant and growing healthcare problem.1,5,7
You may have heard the term ‘clogged arteries’ before, but what does this really mean for your cardiovascular health?
Atherosclerosis occurs when fats, cholesterol, and other substances build up inside the arteries, which are the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body. This fat build-up causes an inflammatory process that results in the development of a plaque, which can continue to accumulate and harden within the artery to eventually reduce (stenosis), or completely block (embolism), the flow of blood.8
These atherosclerotic plaques can occur anywhere in the body. If they affect the arteries in the heart, this results in coronary heart disease. When blood vessels in the brain are affected by atherosclerosis, it can result in cerebrovascular disease, and if it affects the arteries in your legs it is known as peripheral artery disease.
High levels of cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes and obesity all increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis,3 but it is often symptomless for years before it can cause a devastating and life-changing event, such as a heart attack or stroke.4 However, the slow development of atherosclerosis also gives a unique opportunity for prevention.
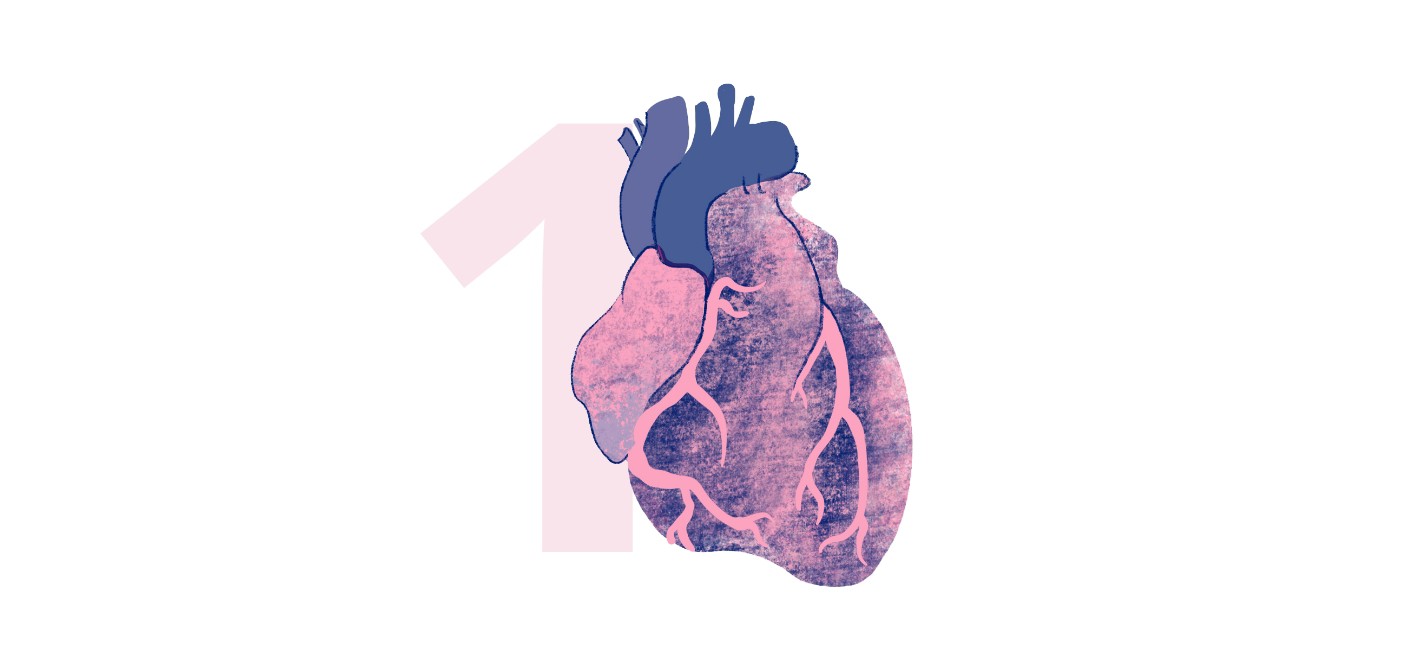
Coronary heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease, is characterised by the build-up of atherosclerotic plaques in the heart’s arteries. As these plaques grow, they can reduce or even rupture and fully block the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, resulting in a heart attack.9
Some of the most common risk factors for coronary heart disease include smoking, obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol levels, and high blood pressure.10
A heart attack occurs when the heart muscle is severely deprived of oxygen due to reduced or completely blocked blood flow in coronary arteries supplying the heart.11
Heart attack symptoms include discomfort in the center of the chest that can last for more than a few minutes, or come and go and change in intensity. It can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain in the chest, or as discomfort in areas of the upper body such as the arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach.12

In order to function properly, the brain needs a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients, which are supplied through blood vessels leading to the brain.13 The group of conditions that affect these blood vessels, and in turn the blood supply to the brain, are called cerebrovascular disease.14
A primary cause of cerebrovascular disease is atherosclerosis, where the formation of fatty deposits called plaques can lead to blood vessels in the brain becoming narrow (stenosis), the formation of a clot (thrombosis), an artery becoming blocked (embolism), or a blood vessel rupturing (hemorrhage).14 Stroke is one of the most common causes of death and a leading cause of disability.15
High blood pressure, smoking, obesity, poor diet, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels can all increase the risk of developing cerebrovascular disease.14
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel supplying the brain with oxygen is blocked by an atherosclerotic plaque (this is called an ischaemic stroke) or if a blood vessel bursts (haemorrhagic stroke).15 The part of the brain that does not get enough blood or oxygen becomes damaged and starts to die within minutes, and can cause long-term brain damage, disability, or even death.13
The signs and symptoms of a stroke usually begin suddenly, so it is important to remember the F.A.S.T. warning signs to spot a stroke:18
- Face drooping or numbness on one side of the face – their smile might be uneven
- Arm weakness or numbness – ask them to raise both arms; one arm might drift downward
- Speech difficulty – they may have slurred speech
- Time – call emergency services right away if you spot any of these signs
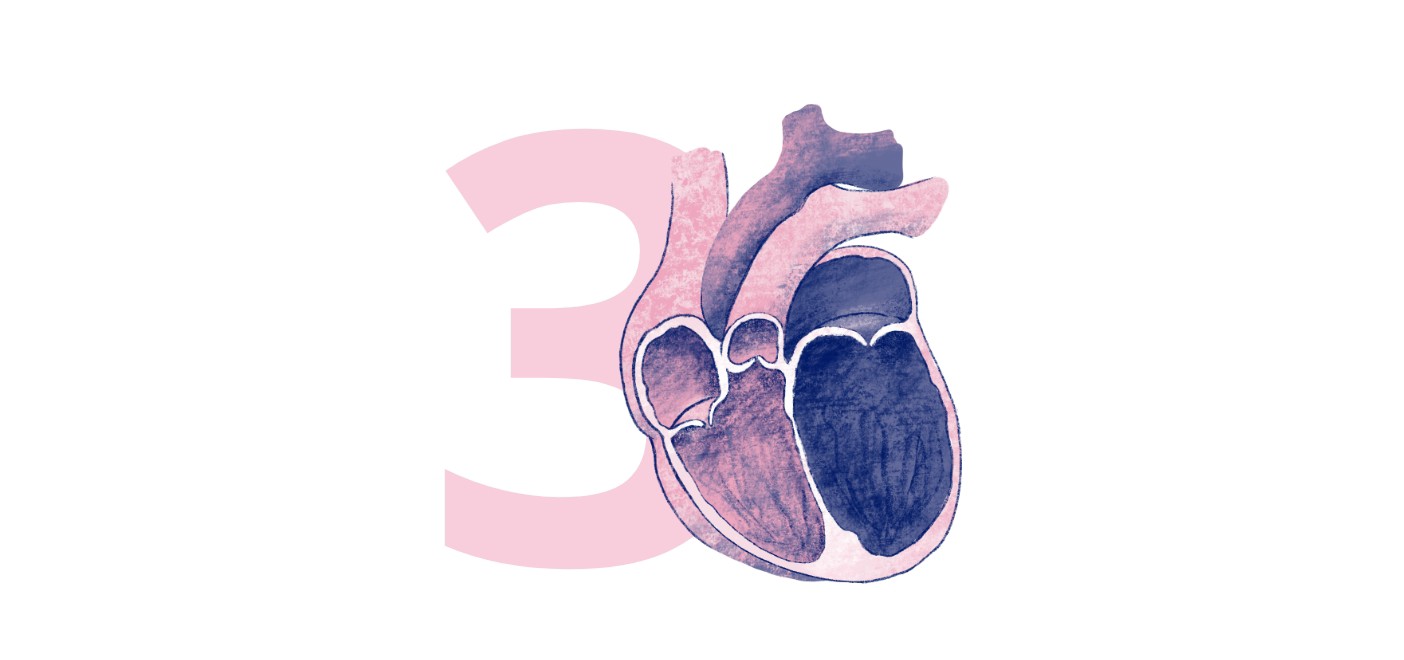
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive condition in which the heart muscle cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s need for blood and oxygen.16 Initially, the heart tries to compensate by pumping harder, causing it to become enlarged. This makes it difficult for the heart to efficiently pump blood throughout the body and eventually, it will worsen until the heart cannot keep up.16
Symptoms of heart failure include feeling constantly tired, shortness of breath, persistent coughing or wheezing, and increased heart rate, which may feel like your heart is racing.16
Both coronary heart disease and high blood pressure are major risk factors for heart failure.14
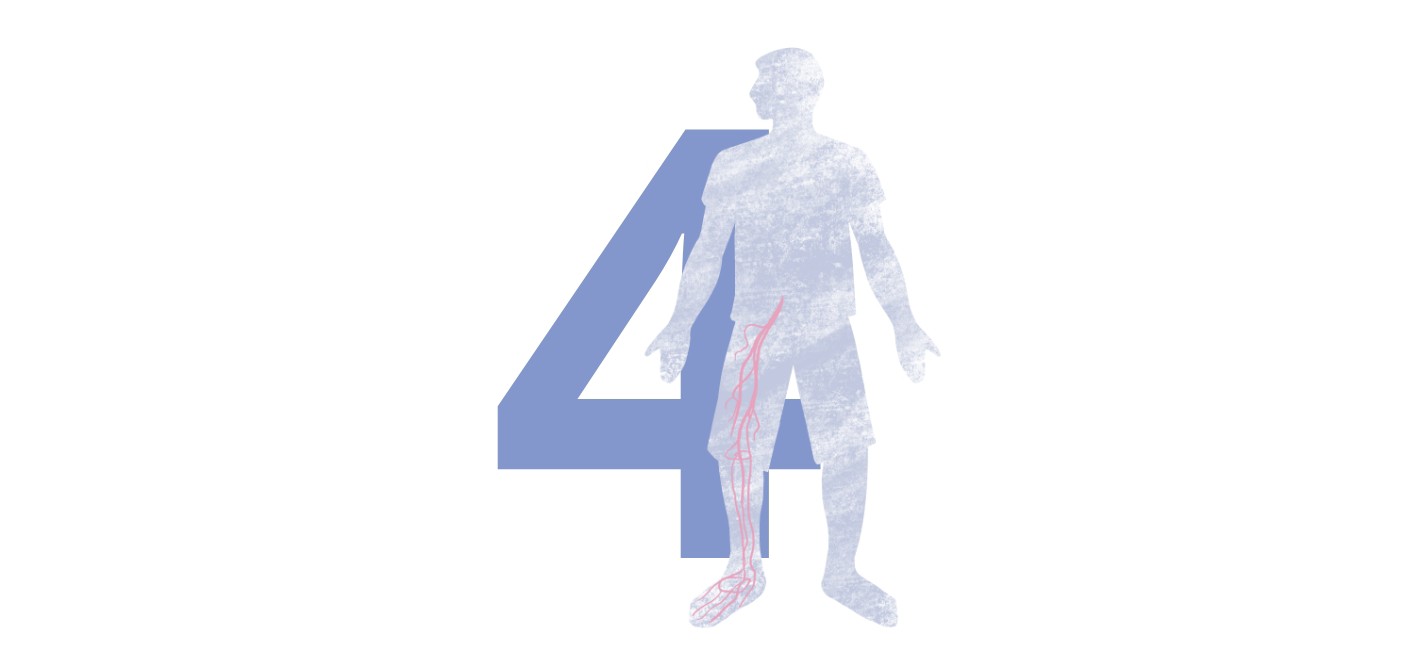
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) occurs when the blood vessels that supply parts of the body, other than the heart or brain, become narrowed or blocked.19 This is primarily caused by the build-up of fatty deposits called atherosclerotic plaques in the walls of these arteries and most commonly affects the arteries leading to the legs and lower body.19
The most common symptoms of PAD include leg pain when walking, which resolves with rest, ulcers that do not heal, and cold or numb toes in the affected leg.20 However, up to 50% of people with PAD do not experience any symptoms.21
Smoking and diabetes are two of the most important risk factors for PAD, with age, family history, inactivity, high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure and obesity also increasing risk.22
1. World Health Organisation. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). WHO factsheets. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About heart disease. Published Published May 15 2024. Accessed May 27 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/heart-disease/about/index.html
3. Frostegård J. Immunity, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. BMC Med. 2013;11(1):117. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-117
4. National Institute of Health (NIH). Atherosclerosis. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/atherosclerosis
5. Barquera S, Pedroza-Tobías A, Medina C, et al. Global overview of the epidemiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Arch Med Res. 2015;46(5):328-338. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2015.06.006
6. Powell-Wiley TM, Poirier P, Burke LE, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(21):e984-e1010. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000973
7. Leal J, Luengo-Fernández R, Gray A, Petersen S, Rayner M. Economic burden of cardiovascular diseases in the enlarged European Union. Eur Heart J. 2006;27(13):1610-1619. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi733
8. Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(16):1685-1695. doi:10.1056/NEJMra043430
9. American Heart Association. Coronary artery disease - coronary heart disease. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/consumer-healthcare/what-is-cardiovascular-disease/coronary-artery-disease
10. Hajar R. Risk factors for coronary artery disease: historical perspectives. Heart Views Off J Gulf Heart Assoc. 2017;18(3):109-114.doi:10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_106_17
11. American Heart Association. What is a heart attack? Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/about-heart-attacks
12. American Heart Association. Warning signs of a heart attack. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/warning-signs-of-a-heart-attack
13. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About stroke. Published May 15 2024. Accessed May 27 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/about/index.html
14. Cerebrovascular disease: causes, symptoms, and treatment. Published August 2, 2019. Accessed February 2, 2022. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/184601
15. American Stroke Association. About Stroke. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke
16. American Heart Association. What is heart failure? Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-failure/what-is-heart-failure
17. Velagaleti R, Vasan RS. Heart failure in the 21st century: Is it a coronary artery disease problem or hypertension problem? Cardiol Clin.2007;25(4):487-v. doi:10.1016/j.ccl.2007.08.010
18. American Stroke Association. Stroke symptoms. Accessed March 14, 2022. https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/stroke-symptoms
19. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Published May 15 2024. Accessed May 27 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/heart-disease/about/peripheral-arterial-disease.html
20. Creager MA, Loscalzo J. Arterial diseases of the extremities. In: Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Loscalzo J, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 20e. McGraw-Hill Education; 2018. Accessed February 2, 2022. accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?aid=1155975428
21. Violi F, Basili S, Berger JS, Hiatt WR. Antiplatelet therapy in peripheral artery disease. In: Gresele P, Born GVR, Patrono C, Page CP, eds. Antiplatelet Agents. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Springer; 2012:547-563. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-29423-5_22
22. Cohoon KP, Wennberg PW, Rooke TW. Diagnosis and management of diseases of the peripheral arteries. In: Fuster V, Harrington RA, Narula J, Eapen ZJ, eds. Hurst’s The Heart, 14e. McGraw-Hill Education; 2017. Accessed February 2, 2022. accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?aid=1161720931
23. American Heart Association. 2021 Heart disease and stroke statistics update fact sheet. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.heart.org/-/media/phd-files-2/science-news/2/2021-heart-and-stroke-stat-update/2021_heart_disease_and_stroke_statistics_update_fact_sheet_at_a_glance.pdf
24. Mathers CD, Loncar D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006;3(11):e442. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030442
25. American Heart Association. CDC Prevention Programs. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.heart.org/en/get-involved/advocate/federal-priorities/cdc-prevention-programs
26. NHS. Cardiovascular disease. Published October 17, 2017. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/cardiovascular-disease/